connected to the op-amp with three different frequencies. Power supplies voltage of op-amp are ± 5v.
 |
Figure 1: An Inverting Differentiator Op-amp |
According to Volt/div of oscilloscope (measured voltage), Vin = 200 mv and Vout = 1000.25 mv
Vin = Asin(ωt) , Vout = Aω cos(ωt) , ω = 2πf , Vout = -RC dVin / dt , Vout = -(RCAω)*cos(ωt)
If R = 1KΩ and C = 1μF so RC = 10E(-3). Vout = -(0.4π)*cos(ωt) , Vout = -1.257 *cos(ωt).
Output amplitude = -1257 mv.
percent error of output voltage = [(expected voltage - measured voltage) / expected voltage]*100%
percent error = [(1257 - 1000.25) / 1257]*100% = 22.43%
 |
Figure 2: A Sinusoidal Input voltage of 1 KHz |
According to Volt/div of oscilloscope (measured voltage) , Vin = 200 mv and Vout = 2500 mv
Vin = Asin(ωt) , Vout = Aω cos(ωt) , ω = 2πf , Vout = -RC dVin / dt , Vout = -(RCAω)*cos(ωt)
If R = 1KΩ and C = 1μF so RC = 10E(-3). Vout = -(0.8π)*cos(ωt) , Vout = -2.513 *cos(ωt).
Output amplitude = -2513 mv.
percent error of output voltage = [expected voltage - measured voltage| / expected voltage]*100%
percent error = [(2513 - 2500) / 2513]*100% = 0.52%
 |
Figure 3: A Sinusoidal Input voltage of 2 KHz |
iii) f = 500 Hz , amplitude = 200 mv , and offset = 0v
According to voltage div of oscilloscope (measured voltage), Vin = 200 mv and Vout = 500 mv
Vin = Asin(ωt) , Vout = Aω cos(ωt) , ω = 2πf , Vout = -RC dVin / dt , Vout = -(RCAω)*cos(ωt)
If R = 1KΩ and C = 1μF so RC = 10E(-3). Vout = -(0.2π)*cos(ωt) , Vout = -0.6283 *cos(ωt).
Output amplitude = -628.3 mv.
percent error of output voltage = [expected voltage - measured voltage| / expected voltage]*100%
percent error = [(628.3 - 500) / 628.3]*100% = 20.42%
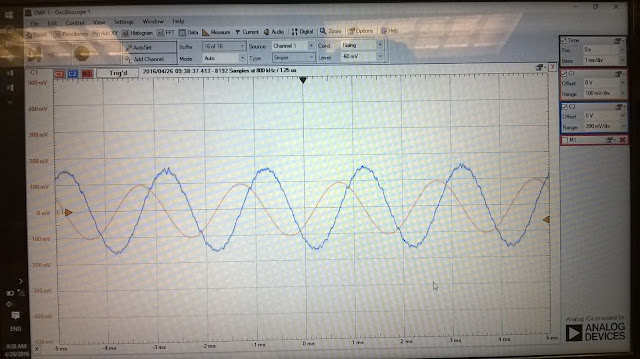 |
Figure 4: A Sinusoidal Input voltage of 500 Hz |
error is less than others low frequencies. In other words, percent error of output voltage decrease
when frequencies increase.
|
Frequency (Hz)
|
Input Voltage (mv)
|
Expected Output Voltage (mv)
|
Measured Output Voltage (mv)
|
Percent Error%
|
|
500
|
200
|
500
|
628.3
|
20.42
|
|
1000
|
200
|
1257
|
1000.25
|
22.43
|
|
2000
|
200
|
2513
|
2500
|
0.52
|
 |
Figure 5: A Schematic of an Inverting Differentiator Op-amp |
Vin = Asin(ωt) , Vout = Aω cos(ωt) , ω = 2πf , Vout = -RC dVin / dt , Vout = -(RCAω)*cos(ωt)
If R = 1KΩ and C = 1μF so RC = 10E(-3).
If f = 1 KHz. Vout = -(2π)*cos(ωt) , Vout = - 6.28 *cos(ωt).
Amplitude of output voltage is equal - 6.28 v that is bigger than power supply voltage (± 5v).
 |
Figure 6: An Inverting Differentiator Op-amp in Saturation Situation |
No comments:
Post a Comment